LPX Dynamic Global Vegetation Model
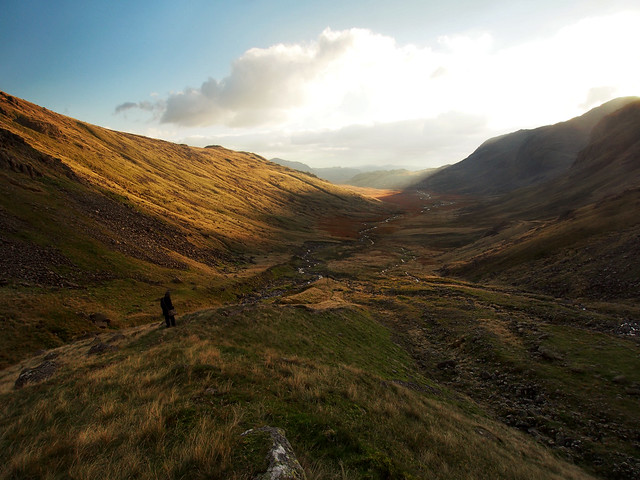
The “Land surface Processes and eXchanges” (LPX: Kelley et al., 2014; Prentice et al., 2011) is a coupled process-vegetation model derived from the LPJ Dynamic Global Vegetation Model family (LPJ-DGVM: Sitch et al., 2003). The model describes dynamical vegetation and terrestrial biogeochemical processes, and how these processes interct with climate to control wildfire disturbance. The model has been developed and benchmarked for Australian fire regimes and fire adapted vegetation Kelley et al., 2014 - incorporating vegetative resistance and reliance adaptations common to Australia but important for the rest of the world - evolutionary adaptive bark protection and post-fire resprouting. The next stage of model development will focus on improving the simulation of fire dynamics for the rest of the world.